Learn the Turkish Alphabet to Reach Fluency
The Turkish language is truly fascinating to learn. Spoken by 88 million people, this language isn’t just limited to the country of Turkey. Millions of people speak it in Germany, Cyprus, and Bulgaria too. So, if you want to learn it, the best way to start is to learn its alphabet. So, what makes the Turkish alphabet so special? Find out everything you need to know about Turkish letters and numbers in the writing system.
The Basics of the Turkish Language
Turkish is a very old language. The first written evidence of Turkish dates back to the 11th century. Turkish is part of the Turkic language family. This means that it’s related to Azerbaijani, Turkmen, Qashqai, and Gagauz.
Today, Turkish is the official language of three countries: Turkey, Northern Cyprus, and Cyprus. However, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Greece, Iraq, Kosovo, North Macedonia, and Romania all recognize Turkish as a minority language. What Kind of Alphabet Does Turkish Use?
Does Turkish Use Latin Letters?
Through the Ottoman Empire, Turkish and Arabic were connected for hundreds of years. So, it’s no surprise that for the majority of the history of the Turkish language, the writing system was closely related to Arabic. The Ottoman Turkish script was very close to Modern Arabic.
But, in 1928, Mustafa Kemal Atatürk replaced Arabic script with the Latin alphabet. Therefore, the Ottoman Turkish scripts was completely abandoned. Today, Turkish is written with Latin letters. Although slight variations exist between the Turkish and the English alphabet, they’re largely the same.

How Many Letters Are in the Turkish Alphabet?
There are 29 letters in the Turkish alphabet. 21 consonants and 8 vowels. Since it’s based on Latin letters, you’ll be familiar with most of them. But, there are a few unique letters in the Turkish alphabet too.
“Ç”, “Ş”, “Ğ”, “I”, “İ”, “Ö”, “Ü” are modified letters to fit the Turkish pronunciation better. Don’t worry, these aren’t completely new sounds. You probably use them every day in English. However, Turkish pays special attention to them as separate letters. If anything, knowing these letters will make learning Turkish easier for you.
The Turkish Alphabet (Türk Alfabesi)
Without further ado, here are the letters of the Turkish alphabet. This funky picture can show you exactly what upper and lower case Turkish letters look like. You can also see them in examples from Turkish words.
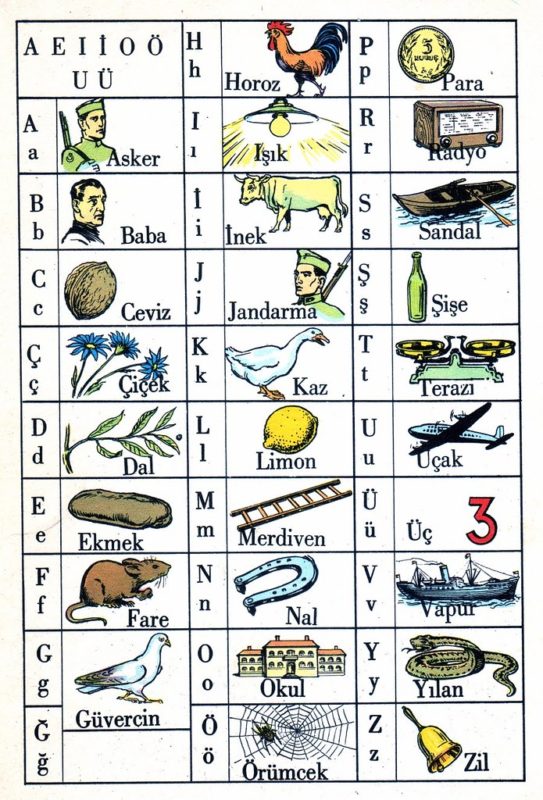
Special Characters and Letters in Turkish
If the unique letters weren’t enough, here are all the special characters Turkish written language uses. These vary from different pronunciations to different uses.
- â, î and û: the little circumflex on top of these vowels serves two purposes. They’re either there to make the sound of the vowel longer. Or they’re there to distinguish words that have the same spelling, but different meaning. (kar /kar/ (snow), kâr /kʲar/ (profit))
- e: the pronunciation of “e” changes to [ɛ~æ] when it’s in front of the letters “m”, “n”, “l”, or “r”.
- g: the pronunciation changes to [ɟ] when it’s next to “e”, “i”, “ö” or “ü”
- k: the pronunciation changes to [c] when it’s next to e, “i”, “ö” or “ü”
- ğ: this letter is actually usually silent after “e” and “i”(değil [ˈde.il] (not)). Occasionally, it can be pronounced as [j] (eğri [ej.ˈɾi] (curve)). And finally, this Turkish letter also makes vowels longer (bağ [ˈbaː] (bond)).
- l: pronounced as [ɫ] when it’s next to next to “a”, “i”, “o” or “u”
- h: pronounced as [ħ] before consonants and at the end of words
- Q, X, W: these letters are not part of the Turkish alphabet because no Turkish word has them. But, you’ll see them in loanwords from English.
Turkish Numbers
Today, Turkish numbers are the same as English numbers. Since the Western world uses Arabic numbers for mathematics, this similarity is clear.
sıfır |
bir |
iki |
üç |
dört |
beş |
altı |
yedi |
sekiz |
dokuz |
on |
0 |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
10 |
How to Learn the Turkish Alphabet
Learning the Turkish alphabet isn’t difficult. You can do it very fast by using one (or all) of these methods:
- Use Spaced Repetition: Spaced repetition is the key to remembering your lessons. By periodically reviewing your material (in this case, the Turkish alphabet), you’ll commit the letters to memory. After a few days, come back to this lesson, and remind yourself of the Turkish alphabet. The more you review, the easier it will be to recall.
- Think of Mnemonics: Come up with Turkish words that start with the letters of the alphabet. By remembering that “A” is for “asker” (soldier), you won’t just remember the spelling, use and pronunciation of Turkish letters. You also grow your vocabulary.
- Sing Songs: Arguably the most effective way to master the Turkish alphabet is to sing the alphabet song. The melody will get stuck in your head, and the constant singing will enforce spaced repetition too. Not to mention the importance of speaking. You should always repeat your Turkish lessons out loud to reach fluency. And what better way to do that than to sing? Use this song to learn the Turkish alphabet quickly:
Start Learning Turkish Today
Mastering the alphabet is your first step to fluency. If you truly want to learn Turkish effectively, you need a reliable language learning method. One that gets you to fluency fast. And that’s why OptiLingo offers.
OptiLingo is the app that’s built on scientifically-proven methods. It gives you the most useful Turkish vocabulary, so you can learn exactly how the locals speak. You’ll reach fluency faster by getting comfortable with Turkish. Start your Turkish language learning right when you download OptiLingo today!