Korean Culture: An Overview
Learning Korean is becoming increasingly popular. Currently, 51 million people live in Korea, yet over 75 million speak the language. This is because Korean popular culture has swept the world. From K-Pop to Korean Dramas, you can easily find Korean culture everywhere. And after an unprecedented victory at the Oscars in 2020, it’s clear that Korean culture is here to stay. To help prepare your language learning journey, here is a quick overview of the most important parts of Korean culture.
Why should you learn about a culture when studying a language? Language exists to help communicate ideas and reflect culture. Language goes hand-in-hand with the culture. And by studying it, you’ll get a better understanding of the “why” behind your lessons. Plus, by engaging with the culture, you get more language learning opportunities. Art, videos, music, and sports all present more interesting paths to fluency than language lessons alone can provide.
Korea’s Role in East Asia
Korea’s neighboring countries are China, Russia, and Japan. These connections give background into the history of its traditions. Chinese sounds and characters have had a great influence on the Korean language. Although Hangul letters are purely Korean, they do borrow Chinese characters to write Korean words called Hanja. (They even have Korean pronunciation).
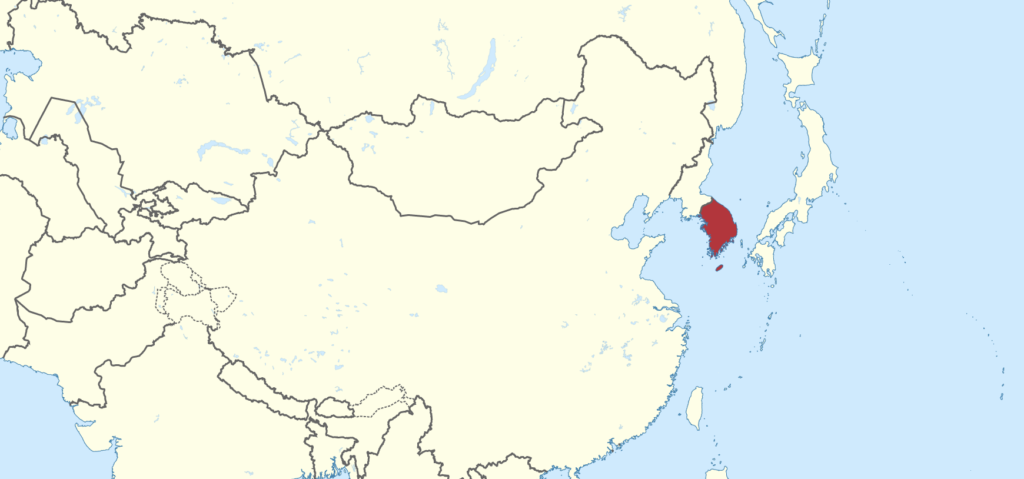
The Korean peninsula is currently divided into South Korea and North Korea at the 38th parallel. There you can find widespread military installations. Although South Korea’s slightly smaller geographically, it has nearly double the population. And traveling there is an amazing and enriching experience.
However, North Korea can be a dangerous country to visit, so it’s not recommended to travel there. Still, there are plenty of places for you to practice your Korean language skills.
The Korean Language
Koreans share one language, with approximately 75 million people around the globe speaking Korean. The language structure, grammar, and vocabulary are similar to Japanese. Korea has one of the highest literacy rates in the world due to the phonetic nature of the written language called Hangul.

Hangul is in the Altaic language family. Apart from the standard Korean language, there are numerous dialects within the peninsula. It is highly respected for being one of the most logically constructed languages in the world. Put together by King Sejong in 1446, the Korean alphabet is very easy to learn. It’s also a featural writing system, meaning that the letters mimic the shapes your mouth, teeth, and tongue make when pronouncing the letters.
Korean Food
Korean cuisine is rich in taste and traditions. Most meals are largely based on rice, vegetables, and meats. Common names of traditional dishes originate from the number of side dishes (반찬; 飯饌; banchan) next to steamed rice. Kimchi is often served with meals. And most Korean dishes often include common ingredients, such as sesame oil, ginger, soy sauce, pepper flakes, and napa cabbage.
Ingredients and traditional dishes differ between regions and provinces. While some regional dishes have gained national popularity, the royal court traditionally brought these specialties together for the royal family.
Korean cultural etiquette is very important in both making and eating food. For instance, the use of chopsticks is necessary for eating anything except soup. And chopsticks are to be placed by the bowl or plate when not using them, not on the plate or in the bowl. It’s also polite to let those older eating first. People use the phrase, Jalmeokgesseumnida (잘먹겠습니다) or “I eat will eat well,” as a common compliment for the chef before eating as well.

Respect and Traditions Between Korean People
It’s important to understand that Korean culture has a foundation of centuries of tradition. Cultural norms are hard to change. Although Western culture had a great influence on Korea in recent decades, the value of respect is deeply rooted in many traditions.
Korean people are incredibly helpful, especially with older people. Showing respect is very important. This is even more prevalent in rural areas where traditional housing is still very popular. The Korean language has built-in formality relating to the social status that will never change. Due to this, Korean tradition will live on.
Birthdays are also recognized differently in Korea. Koreans count themselves as being one-year-old at birth. This may confuse some Westerners. And it’s common to meet a Korean who was born in the same age as you but describe themselves as older.
What Is the Concept of “Face” (Chaemyoun)?
Asian cultures often put a lot of importance on the concept of face (know as chaemyoun in Korean). This signifies reputation, influence, dignity, and honor. They considered disguising one’s true feelings and putting on a stoic face respectable. Especially in the hardships of the 20th century, Korean emphasized the importance of chaemyoun.
Although nowadays this tradition is still alive, younger generations are less concerned about hiding their emotions. Their gestures and facial expressions often reveal how they feel.
The Role of Confucianism in Korean Society
Confucianism is a philosophy that developed from the teachings of the Chinese philosopher Confucius. This school of thought is very prevalent in Korean culture. At the core of Confucianism is social values. It’s a recipe for healthy human relationships is maintaining and respecting the hierarchy between people.
Human connections are often unequal. For example, a ruler and his subject, a boss and an employee, a father and son. According to Confucianism, accepting, and respecting this hierarchy is crucial. Only then can people live in harmony.
This, of course, doesn’t mean that the dominant person receives all the benefits. Both sides of the hierarchy need to give the other something. Whether it’s protection, compassion, or guidance, the dominant role needs to provide equally.
The Importance of Education in Korea
Having a good education is crucial in Korean society. Consequently, the Koreans are very well-educated. Parents often push their children to get into top schools. Starting already from primary school. Unlike in the United States, Koreans put a lot of emphasis on excellent high-school education.
High schoolers in South Korea are constantly studying for university entrance exams. Korean parents will be most happy if their child gets into a top university. Koreans also start studying English at primary school. Many people continue to study it through undergraduate school as well.
Religion in Korean Culture
Christianity is very popular in South Korea. You can find churches everywhere. In fact, Korea houses some of the world’s largest Christian churches.
Buddhism has older roots than Christianity in Korea. It originated from the Mahayana Buddhist practice. As Korea has modernized, its influence has waned. However, there are still plenty of temples in the country, and there’s a visible Buddhist influence in everyday Korean culture.

How Important are Holidays in Korea?
Holidays are an opportunity for families to get together, exchange gifts, and practice traditions. Korean holidays are the same. The importance of family and traditions in Korea means that holidays are hugely appreciated.
Koreans have two New Year Celebrations. They celebrate both the Lunar New Year and the Western Calendar New Year. January 1st is a national holiday in Korea. People get the day off to celebrate “Jesa”. In this ceremony, they write the names of ancestors onto a board. Afterward, family members present offerings and bow to deceased relatives, then they burn the names and families as they reminisce about happy memories. Koreans will also eat a traditional soup called Duk Gook with kimchi on New Year’s Eve.
The Lunar New Year typically occurs in February. Koreans celebrate it in a traditional dress called Hanbok. It’s common to exchange gifts on this holiday. Both New Year holidays are extremely busy times in Korea.
South Korea also celebrates its language on Hangul Day on the 9th of October. In North Korea, it’s celebrated on January 15th. This holiday represents a celebration of the Korean language.
The Korean Independence Day is on March 1st. On this date in 1919, Korea officially declared independence from Japan. There is an official ceremony with the president, tons of activities, and people are encouraged to display the Korean flag on buildings and homes.
Koreans also love romantic holidays. In fact, they have three separate holidays to express love: Valentine’s Day, White Day, and Black Day. On Valentine’s, women give gifts to men. On White Day, the opposite occurs. So, what is Black Day? Black Day is for all those who were left out! On Black Day, friends go out together and eat black noodles in honor of the holiday.
Performance Art and Sandae
Entertainment has deep roots in Korea. Villages and provincial towns have long adored traveling troupes, puppeteers, and jugglers. One of the oldest of these theatre acts is the Korean masked dance called sandae.

This theatre act was usually performed by traveling troupes of local folk bands (but only males). Masks made of paper or gourds cover dancers’ faces. And they paint these props to represent traditional characters in plays. Monks, shamans, noblemen, and young girls are some examples of such tropes.
Today, sandae is still performed in villages in South Kyŏngsang province, as well as some parts of North Korea.
Korean Sports and Recreation
Sports are very important in Korea. Martial arts are particularly deep-rooted in Korean culture. Tae kwon do and ssirŭm (belt-wrestling similar to Japanese sumo) both originate from Korea.
But they also adopted and excel at other sports. Short-track speed skating, football (soccer), and baseball are some of the most popular sports. In fact, South Korea hosted the Summer Olympic Games in 1988, and more recently the Olympic Winter Games in 2018.
Korean fans are famous for their enthusiastic support for their teams. South Korea’s national parks are also a great environment for hikers and campers.
Impact of Korean Culture on the World
The popularity of Korean culture in the world is steadily growing. Korean art attracts millions of visitors every year. Young talents in popular culture have become a driving factor for Korea’s public image and tourism. Pop music generally referred to as K-Pop has international fans.
What started with Psy’s massive hit, Gangnam Style has grown into a global phenomenon and a multi-billion dollar industry. Mainly consisting of groups, these bands feature dancing and singing talent.
Arguably, the most influential K-Pop group is BTS. This boy band made history by topping the Billboard 200 albums chart with their 2018 album “Love Yourself: Tear”. Its title song “Fake Love” was number 10 on the Hot 100 singles chart.
Korean dramas are also hugely popular, and they’re gaining increasing international attention. Korea’s unique film industry now holds multi-Academy Award winner Bong Joon Ho and BAFTA winner Park Chan-Wook in its hall of fame.
Korean Culture and Language Learning
This overview of Korean culture is just the tip of the iceberg. Korea is home to unique customs and traditions that could fill a library. As you progress in your language learning, you will undoubtedly encounter some of these amazing and fascinating parts of Korean culture. The respect and history of the language are deeply rooted in the country’s traditions. And to experience that, you need to work toward Korean fluency.
To get the best chance at speaking Korean fluently, you need OptiLingo. This language learning method is scientifically proven to bring you to fluency in record time. Speak like a local by understanding high-frequency phrases perfectly. The app presents Korean expressions in a stress-free environment, so you can learn at your own pace. Reach fluency confidently with OptiLingo.