Learn About All the German Dialects
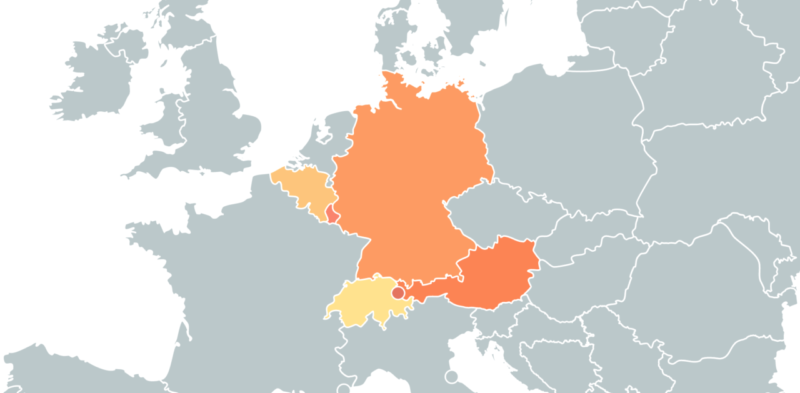
Dialects make a language unique. The regional differences aren’t just exciting, they provide an insight into the culture. Like most widely spoken languages, German has many different dialects. It’s easy to see how Germany, Austria, and Switzerland all have their unique accents. But there are different regional dialects even within Germany. But, which one is worth learning? Here are all the German dialects and accents you need to know of.
1. High German (Hochdeutsch, standard German)
Germany is divided by several different dialects. We categories them as two major ones: High German and Low German. Of these, High German is more important.
This dialect is more commonly known as Hochdeutsch. You may think that High German comes from Northern Germany, but the opposite is the case. Hochdeutsch originates from Southern Germany, where the Alps and highlands are.
Today, this is the standard German you know. Hochdeutch is the dialect they teach in school. If you’re watching German TV or the news, the actors and presenters probably speak this dialect. This is the most commonly spoken German dialect.
2. Low German (Plattdeutch)
Ironically, Low German comes from the Northern part of Germany and the Netherlands. It’s very close to Hochdeutsch in terms of pronunciation. The written forms of the two dialects are completely the same. Low Deutsch is a disappearing dialect because fewer and fewer people speak it.

3. Swiss German (Schwiizerdütsch)
Swiss German is the dialect of Switzerland, naturally. Since French and Italian are also official languages of Switzerland, this German dialect is much different than the others. The neighbouring languages certainly made their impression on the pronunciation. Understanding the Swiss-German dialect is difficult, even for German speakers from other regions.
4. Bavarian German (Bayerisch)
Bavaria is in Southeastern Germany, and Bayerisch is very similar to standard German when written, but differs in the pronunciation of vowels. Everyone in Bavaria can read, write, and understand standard German. But, they rarely have the opportunity to speak it. This is why standard German/Hochdeutsch earned the nickname “Schriftdeutsch” or “written German” in this region.
5. Austrian German (Österreichisches Deutsch)
Austrian German is slightly different from the rest. While it’s mostly the same in grammar, Austrian German has a unique vocabulary. Think of it as American and British English. Americans say chips, and Brits say crisps. But both accents know what the other is talking about. The same goes for the dialects of Austria and Germany. For example, the word for plum in Hochdeutsch is “Pflaume”, while in Austrian German it’s “Zwetschge”.
If you want to listen to the difference between Austrian and Hochdeutsch, this video is very interesting to listen to:
6. Upper Saxon Dialect (Sächsisch)
Saxony is a state in the eastern region of Germany, thus Säschsisch is primarily spoken in the east. It is fairly similar linguistically to standard German and other dialects, but it has an accent that many German speakers have strong feelings about (like how many Brits dislike American accents).
7. The Berlin Dialect (Berlinerisch)
Berlin is the capital of Germany. With its rich history and booming art scene it’s grown into an international hub. So, the accent that the Berlin dialect represents is slowly fading away. As the modernization of Berlin makes it a global city, only a few people live there for their entire lives. The prominence of standard German in education also diminishes from its popularity.
8. Pennsylvania “Dutch” (Pennsilfaanisch Deitsch)
We wanted to include a dialect that’s a little closer to home. Not many know that Pennsylvania Dutch is actually a German dialect. “Dutch” is actually supposed to be “Deutsch”. Formed by German immigrants, this American minority language is still alive on the Eastern coast.
How Do German Dialects Sound?
These descriptions of course can’t show you how different the German dialects sound. Even within Germany, the pronunciation of these accents differs a lot. Don’t believe me? Check out this video of a German girl imitating 12 different German accents:
Which is the Sexiest German Dialect?
Well, decide for yourself. This video below is quite funny as it compares Austrian, Swiss, and Hochdeutsch in terms of sexiness.
Which German Dialect Should I Learn?
Learning a German dialect isn’t really a choice. All of your teaching materials and resources will teach you Hochdeutsch. Every German speaker understands standard German, so that’s your best bet to study. But, if you live in a particular area, you’ll definitely pick up the local accent and vocabulary. Start your German learning journey, and worry about your accent later.
Learn German With the Best App
Whichever dialect you end up choosing, you need to learn German with the most reliable language learning method. One that teaches you proper vocabulary, explains the grammar and makes you speak the language. And that method is OptiLingo.
OptiLingo is the app that makes you fluent the fastest. You won’t waste time learning unnecessary vocabulary, because OptiLingo’s lessons only include the most useful and essential words and phrases in German. You’ll learn to speak exactly as the locals do. Start learning German the right way when you download OptiLingo!