A Summary of the French Language
French is the “language of love”. A fitting name for this gorgeous Romance language. But, there’s a lot more to the French language than pretty sounds. Learn about its origins, history, popularity, and grammar to discover how the French language continues to make its impact on the world.
But French itself has a long and complicated past, one with many twists and turns that led it to be the language it is today. And if you want to gain fluency in this incredibly beautiful, global language, then it helps to have a solid foundation of where French came from to make learning this language easier.
From its history to interesting facts, to the differences between English and French (plus, what makes French so complicated for English speakers), this is everything you need to know about the French language.
The Popularity of French
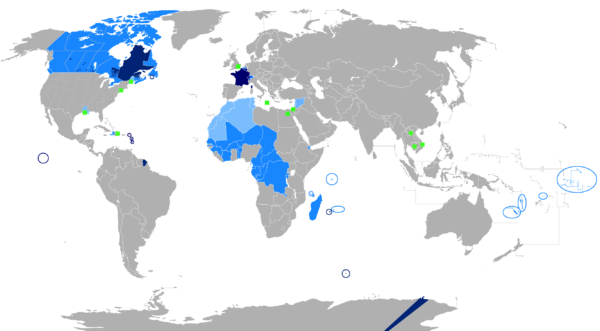
It’s the 16th most spoken language, and the number of French speakers continues to grow. Since 1945, the number of French speakers has tripled to 275 million people with over 77 million people speaking it as their first language. It’s the official language of 29 countries (see chart below). And it’s taught in nearly every country in the world.
French is the only language (apart from English) that’s spoken on every continent.
29 Countries Where French Is the Official Language
- France
- Belgium
- Benin
- Burkina Faso
- Burundi
- Cameroon
- Canada
- Central African Republic
- Chad
- Congo
- Comoros
- Ivory Coast
- Democratic Republic of the Congo
- Djibouti
- Equatorial Guinea
- Gabon
- Guinea
- Haiti
- Luxembourg
- Madagascar
- Mali
- Monaco
- Niger
- Rwanda
- Senegal
- Seychelles
- Switzerland
- Togo
- Vanuatu
French as the Lingua Franca
For quite some time (between the 17th century until WW1), French was the lingua franca. A lingua franca is a language spoken between people who speak different languages. It was the language of diplomats and government throughout Europe. French was so popular, in fact, that the courts of some countries preferred it to their own language.
However, WW1 upset French’s hold on being the lingua franca. And by the end of WW2, English had replaced French and remains the current one. Even so, it still remains an influential language as one of the official languages of the UN, EU, and several other major organizations. It also serves as the main language for deliberations in the European Union’s Court of Justice.
French, a Popular Language in North America
The French language, including its various forms of Haitian Creole, Cajun, and Quebecois, is the fourth most widely spoken language in the United States. Over 1.3 million people speak French in the United States today. Of this, approximately 200,000 residents of the state of Louisiana, 4% of the population, speak mainly French in their homes.
Canada is home to about 8 million native French speakers. The majority of them, around 7 million, live in Quebec, where French is the official language. Montreal is the largest city in Quebec and is the fourth largest French-speaking city worldwide. There are roughly 2 million people in the country that speak French as a second language. The total population is about 33 million, so approximately 30% of the population is proficient in French. Canada is dedicated to bilingualism and has documented this in its Charter of Rights and Freedoms. The country has two official languages, English and French, and the current president, Justin Trudeau, releases all public communication in both languages.
With millions of speakers surrounding you, French is truly a language that’s worth learning. If you’re still looking for reasons to begin your French language learning journey, here are 16 reasons to start learning French.
The Origins of the French Language
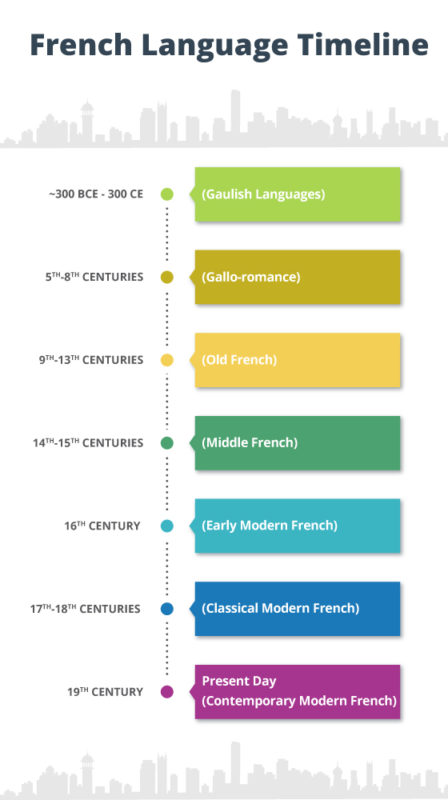
To understand how French became the language it is today, we need to head back in time to around the 2nd century BCE. Back then, the area that is now France belonged to a region known as Gaul. This area included Belgium, Northern Italy, Switzerland, and parts of Germany/Netherlands). And they did not speak French. In fact, French as we know it today wouldn’t arrive for a long time.
Instead, they spoke Gaulish (a variety of Celtic languages and dialects that we know very little about). Then, as most stories of ancient European history go, the Romans showed up. They conquered Gaul in the 2nd century.

True to Roman nature, if you wanted to become a citizen and get anywhere in life, you needed to speak the language and follow Roman customs. As a result, Latin washed over Gaul, eventually wiping out the Gaulish languages.
During this period, there were two varieties of Latin: Classical Latin and Vulgar Latin. Classical Latin is the traditional form of Latin we know and love. This was spoken by those who could read and write. Vulgar Latin was the common person’s Latin. And it varied by region. Over time, these regional variations would form new languages (what we call romance languages today).
Franc Influence on French Language History
Fast forward to 375 CE and Germanic invasions pushed through the Western Roman Empire, establishing Germanic Kingdoms. These kingdoms increased the speed at which Vulgar Latin changed.
Specifically, the Francs are responsible for a huge directional shift of the Latin language in the region. The result of their impact on the French language created what we now refer to as Old French.
Not surprisingly, it originated in the central region of Île-de-France. Sound familiar? Well, it’s where Paris is today. And back then (just like now), Paris was the literary and cultural center.
Then in 1539, the Edict of Villers-Cotterê secured the future of this dialect the core of modern-day French. The edict required laws, legal acts, and contacts to be written in French to avoid confusion. Except, back then they pronounced it as “Fransweè”, not “Francois”.
Still, it would be a while before France held one unified language.
The Spread of French Through Universal Education
Despite all the efforts, until 1881, only a small portion of France actually spoke French until 1881. The passing of the Jules Ferry Laws established free, compulsory education for the people of school. And languages outside of French were banned from primary schools. Under these new laws, even the more rural areas of France quickly adopted French as the main language.
The Role of the Académie Française
If you’ve ever stepped foot inside a French classroom, you talked about l’Académie Française at some point. Founded in 1634 by Cardinal Richelieu, its main goal was to preserve the French language by giving it set rules. By 1694, they published the first French dictionary.
Fast forward to modern times, “l’Académie” works to maintain a precise dictionary of the french language (that they don’t actually sell to the public). Recently, that means resisting the adoption of English loan-words into the language by either modifying them for French or creating French versions. The Academie also updates grammar rules and modern spellings as well.

How Difficult Is French Compared to English?
As a Romance Language, it’s one of the easier languages to learn for English speakers. That’s why the Foreign Service Institute (FSI) ranks French as a Category 1 language. And they estimate that it would take you roughly 575 – 600 hours to reach fluency. However, it’s best to use that as a guideline because judging how long it takes someone to learn a foreign language can be problematic.
Those interested in learning French may benefit from extra tuition with a private tutor. Getting help from a tutor will help you master French speaking and writing skills in a way that online apps cannot. Take a look at reputable tutoring platforms such as Superprof to find a tutor near you. Students simply fill in their search criteria and they can find a list of qualified private tutors close by to help them on their mission to master the French language.
How Similar is French to English?
There are plenty of shocking similarities between English and French. Mainly, this is a result of William the Conqueror’s invasion of England in 1066. As a result, the French rule England for a while, leaving their impact on the language that you can still see today.
Here are some of those similarities:
- Similar alphabets: The English and French languages both use the Latin Alphabet. While there are both 26 letters, there are some differences in pronunciation.
- Similar Sentence Structure: Don’t worry, we won’t get too heavy into French grammar here. But you can rest easy that you’ll find the similar SVO (subject verb object) sentence structure in French as you do in English. Keep in mind that this usually for basic sentences. The more complex they get, the more different from English they become.
- Loanwords: There are a LOT of loan words in French. (Despite French opposition to them). You can hear words like, “Okay”, “Happy Hour”, “Un parking”, and “Un job” pop up in conversations. The Academy has made attempts to create French versions of English words.
- Cognates: These are not quite the same as loan words. Rather, they have similar origins in Latin and as a result look and sound similar in their respective languages. Absolutely and “Absolutement”; Accident and “Acciden”t; Actor and “Acteur”. And these are just the A’s. You can find a much larger list of cognates here.

How Are English and French Different?
The short answer: in a lot of ways. You’ll experience huge differences in the languages with their pronunciation and grammar. French has some sounds unique to it that are difficult for English speakers, strange spellings, and what seems like endless exceptions to grammatical rules. However, if you know what to look for when you’re getting started, you’ll have an easier time seeing progress.
Here are some ways that French and English Differ:
- French nouns have genders: In English, nouns have the same articles because they are gender neutral (unless it’s a living noun with an actual gender). But French is different. French nouns are either feminine or masculine. And if you’re looking for a trick to figure out if a noun is masculine or feminine, sorry to disappoint. A noun’s gender is often arbitrary. You’ll have to memorize the noun with its article.
- Gender also affects sentence construction: Matching gender goes beyond articles. You’ll need to match relative pronouns and adjectives too.
- Adjectives come after nouns: In English, adjectives come first. And they can build on each other to modify a noun. Not in French. In French, you wouldn’t say “the soft, fluffy cat.” You’d say, “the cat soft fluffy.” That difference can also change how you process the image, and shows how learning a new language can alter your perception of reality.
- Negation: There are a few ways to say “no” or “not” in English (think of the prefixes un- and in-). French requires that you bracket negative phrases using two words, “nas” and “pas” (and a few other variations). You’d introduce the phrase with “nas” then add what you’re negating and follow it up with “pas” (or the variation). “Plus”, “rien”, “jamais”, “personne” are other alternatives. And if it helps, you can think of it as negative parentheses.
- False cognates (Faux Amis): Just when you hit your stride and start learning French, you’ll start running into false cognates. These are words that look like English words but mean something completely different. And while some may cause minor confusion, others can cause extreme embarrassment. So, be careful. Words like “formidable” mean “great” (not “fearsome”) and Con vs Con (vulgar term for female genitals). And there are plenty more.
Why Are French Spelling and Pronunciation Different?
It’s a common complaint from French language learners: “Why does French not sound anything like it’s written?” It’s so common (and the answer so interesting) that it needs its own section. In short, the spelling of French words reflects that of Old French of C.1100 – 1200 CE, and it hasn’t changed much.
This is shocking when you realize just how much the French language has changed since then. The “silent” letters you often see were originally pronounced. But over time, pronunciations shifted, leaving France’s orthography behind. In a way, reading French is kind of like looking back in time.
Be careful: A lot of the final consonants in French remain unpronounced. But (like many French grammar rules) there are exceptions. The mnemonic “Be Careful” will help you remember where some of these instances occur: C, R, F, and L. But that’s not always the case.
Liaison: It’s best to think of this as cursive pronunciation. When speaking in french, sometimes, you also pronounce the final consonant if the next word starts with a vowel, “les enfants” wouldn’t be pronounced “le enfants”, but “les enfants”.
It gets more complicated with words that start with silent consonants: petits hommes. You’d pronounce it “petits ommes,” not “peti ommes”. And yes, there are other exceptions to be aware of as well, but those are better saved for later on. When starting out on your language learning journey, don’t get too hung up on grammar. It has its place, but don’t let it overwhelm you.

French Dialects and Accents
There are also numerous dialects and accents in French. France alone has 28 different ones. Outside of France, there are many more. In Canada, for instance, 95% of the population speaks French as either a first or second language. And while it may sound the same to the untrained ear, their dialect is much different than France and quite noticeable between the two. A similar comparison can be made between American English and British English.
The puck doesn’t stop there either. Belgian, Switzerland, Creole, Indian, and numerous countries in Africa all speak varying French dialects that add both subtle and noticeable shifts to the standard version of French found in France.
When you’re learning French, you shouldn’t worry about which accent or dialect you learn. Don’t be concerned with yours either. Just practice your pronunciation as much as you can, and you accent will develop naturally.
Counting in French: It’s Weird
“Quatre-vingt-dix-neuf” is 99 in French. Well, to be precise, it’s “four twenties, ten, nine”. Welcome to French counting. For the most part, counting in French is smooth sailing. They use Arabic numerals, counting very similar to English…until 69. That’s because there’s no word for 70, 80, or 90. 76 translates to sixty-ten-six. 88? Try, “quatre-vingt-huit” or “four-twenties-eight”.
But this isn’t some random, bizarre way to count. IT’s part of something called the “vigesimal system”. And it could have ended up in the French language thanks to the Celtic influence in the region. You see, Romans used a system of 10’s to count, that’s why it’s familiar to us. But, the Celts used systems of 20.
French Numbers:
0 |
zéro |
10 |
dix |
20 |
vingt |
300 |
trois cents |
1 |
un, une |
11 |
onze |
30 |
trente |
400 |
quatre cents |
2 |
deux |
12 |
douze |
40 |
quarante |
500 |
cinq cents |
3 |
trois |
13 |
treize |
50 |
cinquante |
600 |
six cents |
4 |
quatre |
14 |
quatorze |
60 |
soixante |
700 |
sept cents |
5 |
cinq |
15 |
quinze |
70 |
soixante-dix |
800 |
huit cents |
6 |
six |
16 |
seize |
80 |
quatre vingts |
900 |
neuf cents |
7 |
sept |
17 |
dix-sept |
90 |
quatre vingt-dix |
1000 |
mille |
8 |
huit |
18 |
dix-huit |
100 |
cent |
10,000 |
dix mille |
9 |
nuef |
19 |
dix-neuf |
200 |
deux cents |
100,000 |
cent mille |
Learn French Easily
The French language holds a long and impressive history. Today, it’s still one of the most spoken languages in the world. Speaking French fluently can open opportunities for you that you could only dream of before. Luckily, you can learn French very easily and quickly with OptiLingo.
OptiLingo is the language learning app that’s built on scientifically proven methods. It gives you the most common words and phrases, so you learn exactly how the locals speak. Don’t waste your time with unnecessary grammar and vocabulary. Learn French effectively when you download OptiLingo!